Teeth grinding is a prevalent issue that can quietly cause significant damage to your teeth, jaw muscles, and overall oral health. Whether you’re dealing with nocturnal bruxism (grinding during sleep) or awake bruxism, it’s essential to address the issue early to prevent long-term damage. In this guide, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and effective ways on how to stop teeth grinding. With the right approach, you can protect your smile, reduce pain, and enjoy a good night’s sleep.
What Is Teeth Grinding and Why Does It Happen?
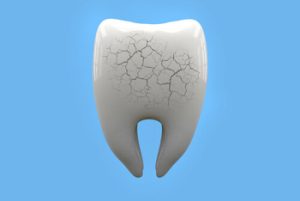
Teeth grinding happens when the upper and lower teeth are tightly clenched or pressed against each other. Although it can occur during the day, it is most frequently associated with nighttime, known as sleep bruxism. Over time, this behaviour can result in jaw pain, tooth wear, and various other issues.
What Causes Teeth Grinding?
 Several factors contribute to bruxism:
Several factors contribute to bruxism:
- Stress and Anxiety: Feeling anxious can cause jaw muscles to tense, leading to grinding.
- Sleep Disorders: Conditions like sleep apnoea and poor sleep quality often coincide with nocturnal bruxism.
- TMJ Disorders: Issues with the temporomandibular joint (where the lower jaw connects to the skull) can increase grinding.
- Lifestyle Habits: Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and even frequent gum chewing can exacerbate grinding.
- Medical Conditions: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), sleep-related disorders, and other health issues may also play a role.
Recognising the Symptoms of Teeth Grinding
Teeth grinding can be hard to detect, especially if it occurs while you sleep. However, common symptoms include:
- Jaw Pain: Persistent soreness or tightness in the jaw muscles.
- Tooth Wear: Flattened or cracked teeth are often a tell-tale sign of severe bruxism.
- Morning Headaches: Frequent headaches upon waking due to jaw muscle tension.
- Facial Pain and Ear Pain: These often accompany TMJ disorders and teeth grinding.
- Tooth Sensitivity: Magnified sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Neck Pain: Grinding can strain muscles in the neck and jaw joints.
- Loose Teeth or Tooth Damage: Excessive grinding can lead to tooth mobility or fractures.
How to Stop Grinding Your Teeth: Practical Solutions
Addressing teeth grinding involves identifying triggers and adopting targeted solutions. Here’s how to stop grinding teeth effectively:
1. Reduce Stress with Relaxation Techniques
Stress reduction techniques are a cornerstone of bruxism management. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can relax the jaw muscles and lessen the tendency to grind.
Quick Tips for Stress Reduction:
- Take short breaks to stretch during work.
- Try progressive muscle relaxation before bed.
- Maintain a journal to manage feelings of anxiety.
2. Adopt Good Sleep Hygiene
Improving your sleep habits can significantly reduce nocturnal bruxism. Maintaining a bedtime routine and creating a comfortable sleep environment can have a notable positive impact.
Tips for Better Sleep Quality:
- Avoid using screens for at least an hour before going to bed.
- Create a dark, quiet, and cool sleeping environment.
- Skip caffeine or alcohol before bedtime.
3. Protect Your Teeth with a mouthguard
Custom-made night guards or occlusal splints are excellent options for preventing tooth damage. These devices create a barrier between the top and bottom teeth, minimising wear.
When to Use a Mouth Guard:
- If you experience severe bruxism or cracked teeth.
- As a preventative measure to protect dental restorations.
- For children who grind their teeth during sleep.
4. Jaw Relaxation Exercises
Practising jaw relaxation exercises can relieve tension in the muscles involved in grinding. A professional can guide you through specific stretches to reduce jaw pain and improve flexibility.
Simple Jaw Relaxation Techniques:
- Place your tongue on the roof of your mouth and let your jaw hang loose.
- Gently massage the temporomandibular joint to reduce muscle tension.
5. Address Underlying Dental Issues
Misaligned teeth or bite issues can exacerbate grinding. Dental correction, such as braces or other orthodontic treatments, may help alleviate the problem.
6. Explore Advanced Treatment Options
For severe cases of bruxism, advanced solutions may be necessary:
- Botox Injections: These can relax overactive jaw muscles.
- Muscle Relaxants: Medications can ease muscle tension in severe bruxism.
- Mandibular Advancement Devices: Often used for sleep apnoea, these devices reposition the jaw to enhance airflow and reduce grinding.
How to Stop Teeth Grinding: Lifestyle Changes
Teeth grinding, or bruxism is often influenced by habits and lifestyle choices. Making targeted adjustments to your daily routine can significantly reduce grinding episodes, protect your teeth, and improve your overall quality of life. Here are some practical lifestyle changes to help you stop grinding your teeth.
1. Reduce Stress Levels
 Stress and anxiety often contribute to teeth grinding. By integrating stress-relief techniques into your daily routine, you can ease jaw tension and reduce the occurrence of bruxism.
Stress and anxiety often contribute to teeth grinding. By integrating stress-relief techniques into your daily routine, you can ease jaw tension and reduce the occurrence of bruxism.
What You Can Do:
- Practise mindfulness or meditation to calm your mind.
- Engage in yoga or gentle stretching exercises.
- Take short breaks throughout the day to relax your facial and jaw muscles.
2. Limit Alcohol and Caffeine Consumption
Both alcohol and caffeine can intensify bruxism, particularly nocturnal bruxism. Reducing your intake can help minimise grinding episodes and improve sleep quality.
Tips:
- Limit caffeinated drinks, particularly during the afternoon and evening hours.
- Restrict alcohol consumption, particularly before bedtime.
3. Avoid Chewing Gum
Chewing gum can overwork the jaw muscles, increasing their tension and making you more prone to grinding. It’s best to skip the gum altogether if you’re dealing with bruxism.
4. Stay Hydrated
Lack of hydration can cause muscle tension and cramps, potentially worsening teeth grinding. Keeping yourself hydrated by drinking water consistently throughout the day helps relax your jaw muscles.
Hydration Tips:
- Keep a reusable water bottle with you to encourage regular hydration.
- Limit sugary or caffeinated drinks that can dehydrate you.
5. Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
A good night’s sleep is essential for reducing teeth grinding, especially sleep bruxism. Establishing a soothing bedtime routine can signal to your body and mind that it’s time to unwind and relax.
Ideas for a Relaxing Routine:
- Read a book or listen to soothing music.
- Enjoy a warm bath to help ease tension in your jaw and facial muscles.
- Use aromatherapy with calming scents like lavender.
6. Improve Sleep Hygiene
Good sleep hygiene is vital for reducing sleep-related disorders, including bruxism. Creating an optimal sleep environment can improve the quality of your sleep and reduce grinding episodes.
Sleep Hygiene Tips:
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends.
- Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
- Avoid screens at least an hour before bed to minimise blue light exposure.
7. Avoid Overworking Your Jaw Muscles
Overusing your jaw muscles can make them more prone to clenching and grinding. Be mindful of your habits during the day and avoid unnecessary tension.
What to Watch For:
- Avoid biting your nails or chewing on pens and pencils.
- Eat soft foods if your jaw feels tense or sore.
8. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise can reduce overall muscle tension and help you manage stress more effectively. Physical activity also promotes better sleep, which can reduce nocturnal bruxism.
Activities to Try:
- Aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, or cycling.
- Low-impact activities like swimming or yoga to relax your muscles.
9. Quit Smoking
Smoking is linked to increased bruxism and other oral health issues. Quitting smoking not only benefits your overall health but can also help reduce teeth-grinding episodes.
10. Focus on Jaw Relaxation
Throughout the day, pay attention to your jaw position and consciously relax it when you feel tension building.
Jaw Relaxation Techniques:
- Rest your tongue on the roof of your mouth to keep your jaw muscles relaxed.
- Perform gentle stretches by slowly opening and closing your mouth.
11. Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bedtime
Consuming large or heavy meals close to bedtime can affect your sleep quality and heighten the risk of nocturnal bruxism.
Tips for Evening Meals:
- Eat your last meal at least two to three hours before bed.
- Avoid spicy or acidic meals that might cause discomfort and disrupt your sleep.
12. Cut Down on Sugar
Excessive sugar can contribute to muscle tension and poor sleep, both of which can worsen teeth grinding.
Better Choices:
- Opt for snacks like fresh fruits or nuts instead of sugary treats.
- Check food labels for hidden sugars.
13. Practise Mindful Awareness
Bruxism often occurs without conscious awareness, especially during waking hours. Practising mindfulness can help you recognise when you start to grind your teeth and allow you to stop the habit.
Mindful Tips:
- Set reminders on your phone to check your jaw tension throughout the day.
- Practice deep breathing to help release tension.
With these lifestyle changes, you can significantly lower the frequency and severity of teeth grinding. For persistent or severe bruxism, consider consulting with a dentist or healthcare provider to explore additional treatment options.
Helping Children Who Grind Their Teeth
Children often grind their teeth as a reaction to stress or developmental changes. While mild bruxism in children typically resolves on its own, severe cases should be addressed with a dentist. Encouraging good sleep hygiene and stress reduction techniques can make a difference.
Preventing Long-Term Damage
Left unchecked, teeth grinding can lead to significant oral health issues, including:
- Tooth Loss: Severe bruxism can weaken teeth over time.
- TMJ Disorders: The strain on the jaw joint can cause chronic pain and dysfunction.
- Tooth Damage: Cracked teeth or extensive wear may require dental restorations.
FAQs About Teeth Grinding
- Can teeth grinding go away on its own?
In some cases, especially in children, teeth grinding may resolve on its own as they grow older. However, for adults or those with chronic symptoms, treatment and lifestyle changes are often needed to stop grinding teeth and prevent complications.
- What are the potential long-term consequences of untreated bruxism?
Untreated teeth grinding can lead to severe tooth wear, cracked teeth, loose teeth, temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ disorder), chronic jaw pain, and even tooth loss. It may also result in poor sleep quality and other health complications.
- What’s the difference between awake bruxism and sleep bruxism?
Awake bruxism occurs during waking hours and is often related to stress or concentration. Sleep bruxism happens during sleep and is typically related to sleep disorders, such as sleep apnoea. Both can cause similar symptoms but may require different management strategies.
- Are there natural remedies for teeth grinding?
Yes, natural remedies like stress reduction techniques, jaw relaxation exercises, and maintaining good sleep hygiene can help reduce symptoms. However, severe cases may require professional intervention.
- Can diet impact teeth grinding?
Yes, dietary choices can impact bruxism. Overconsumption of caffeine or alcohol may intensify grinding while staying hydrated, and following a balanced diet can help relax jaw muscles and alleviate symptoms.
- How can I tell if I grind my teeth at night?
If you wake up with jaw pain, morning headaches, or notice tooth wear, you may have sleep bruxism. A dentist can confirm this by examining your teeth and jaw or recommending a sleep study.
- Can teeth grinding be a sign of another condition?
Yes, teeth grinding is often linked to conditions like sleep apnoea, TMJ disorders, and even attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Identifying and treating these underlying issues can help alleviate bruxism.
- How do night guards work for bruxism?
Night guards provide a protective barrier between the top and bottom teeth, preventing damage caused by grinding. They also help distribute pressure evenly, reducing strain on the jaw joint and surrounding muscles.
- Is teeth grinding hereditary?
 There is evidence to suggest that bruxism can run in families. If you have a family history of teeth grinding or TMJ disorders, you may be more likely to experience the condition.
There is evidence to suggest that bruxism can run in families. If you have a family history of teeth grinding or TMJ disorders, you may be more likely to experience the condition.
- Can teeth grinding cause neck pain?
Yes, teeth grinding can lead to muscle tension that extends beyond the jaw and into the neck and shoulders. This is particularly common in cases of severe bruxism or TMJ disorders.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Teeth Grinding Today
Teeth grinding doesn’t have to damage your smile or overall well-being. By identifying the symptoms, understanding the causes, and implementing tailored solutions, you can stop grinding your teeth and effectively reduce pain.
If you’re struggling with teeth grinding, contact Beyond Infinity Dental at (02) 8806 3799 to explore treatment options and protect your oral health.
References:
Sleep Foundation. (n.d.). Bedtime routine for adults. Retrieved from https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-hygiene/bedtime-routine-for-adults
Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Temporomandibular disorders (TMD): Overview. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15066-temporomandibular-disorders-tmd-overview
Colgate. (n.d.). Botox for bruxism: Learn what’s right for you. Retrieved from https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/bruxism/botox-for-bruxism-learn-whats-right-for-you
MouthHealthy. (n.d.). Water: The best beverage for your health. Retrieved from https://www.mouthhealthy.org/nutrition/water-best-beverage
Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Sleep apnea: Symptoms and causes. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sleep-apnea/symptoms-causes/syc-20377631#:~:text=Overview,you%20might%20have%20sleep%20apnea